ACCESSING ORGANIZATIONAL INFORMATION - DATA WAREHOUSE
In this chapter, we learned about :
- Descibe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data marts in an organization
- Compare the multidimensional nature of data warehouses (and data marts), with the two-dimensional nature of databases
- Identify the importance of ensuring the cleanliness of information throughout an organization
- Explain the relationship between business intelligence and a data warehouse
HISTORY OF DATA WAREHOUSING
- Data warehouses extend the transformation of data into information
- In the 1990's executives became less concerned with the day-to-day business operations and more concerned with overall business functions
- The data warehouse provided the ability to support decision making without disrupting the day-to-day operations
DATA WAREHOUSES FUNDAMENTALS
- Data warehouse - A logical collection of information - gathered from many different operational databases - that supports business analysis activities and decision-making tasks
- The primary purpose of a data warehouse is to aggregate information throughout an organization into a single repository for decision-making purposes
- Extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) - A process that extracts information from internal and external databases, transforms the information using a common set of enterprise definitions, and loads the information into a data warehouse
- The ETL process gathers data from the internal and external databases and passes it to the data warehouse
- The ETL process also gathers data from the data warehouse and passes it to the data marts
- Data mart - Contains a subset of data warehouse information
MULTIDIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND DATA MINING
- Databases contain information in a series of two-dimensional tables
- In a data warehouse and data mart, information is multidimensional, it contains layers of columns and rows
- Dimension - A particular attribute of information
- Each layer in a data warehouse or data mart represents information according to an additional dimension
- Dimensions could include such things as :
- Products
- Promotions
- Stores
- Category
- Region
- Stock price
- Date
- Time
- Weather
- Cube - Common term for the representation of multidimensional information
- Users can slice and dice the cube to drill down into the information
- Cube A represents store information (the layers), product information (the rows), and promotion information (the columns)
- Cube B represents a slice of information displaying promotion II for products at all stores
- Cube C represents a slice of information displaying promotion III for product B at store 2
- Data mining - The process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone
- To perform data mining users need data mining tools
- Data mining tool - Uses a variety of techniques to find patterns and relationships in large volumes of information and infers ruler that predict future behavior and guide decision making
- Data mining can begin at a summary information level (course granularity) and progress through increasing levels of detail (drilling down), or the reverse (drilling up)
- Data-mining tools include query tools, reporting tools, multidimensional analysis tools, statistical tools, and intelligent agents
INFORMATION CLEANSING OR SCRUBBING
- An organization must maintain high-quality data in the data warehouse
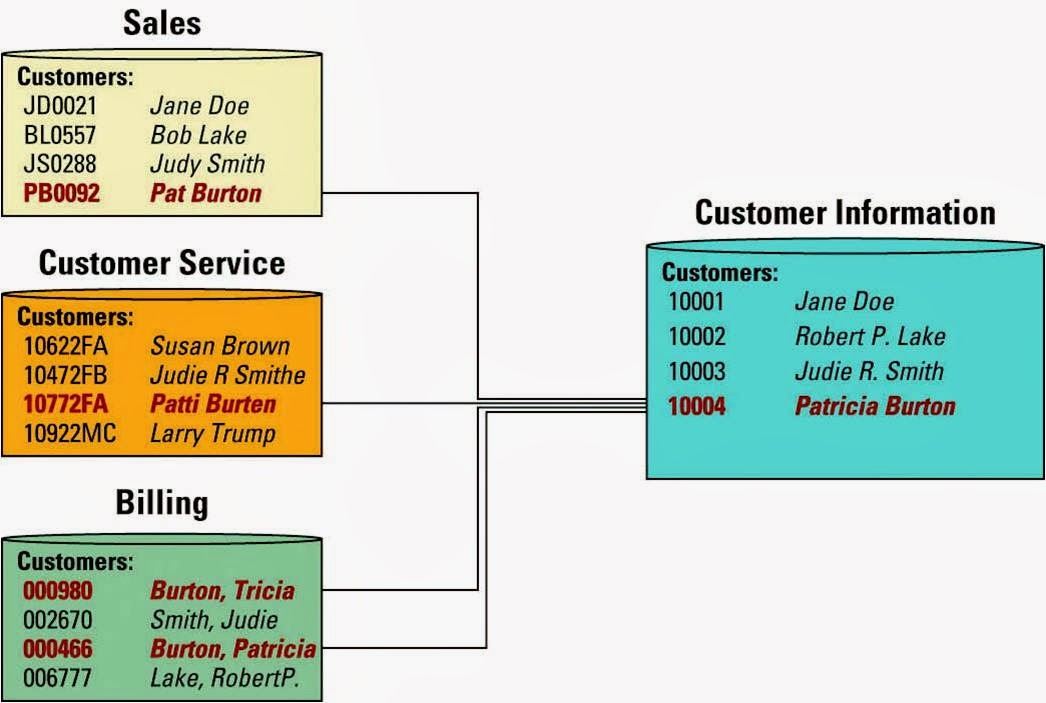
- Information cleansing or scrubbing - A process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or incomplete information
- Contact information in an operational system
- Standardizing customer name from Operational Systems
- Information cleansing allows an organization to fix these types of inconsistencies and cleans the data in the data warehouse
- Accurate and complete information
BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
- Business intelligence - Information that people use to support their decision-making efforts
- Principle BI enablers include :
- Technology
- People
- Culture





No comments:
Post a Comment